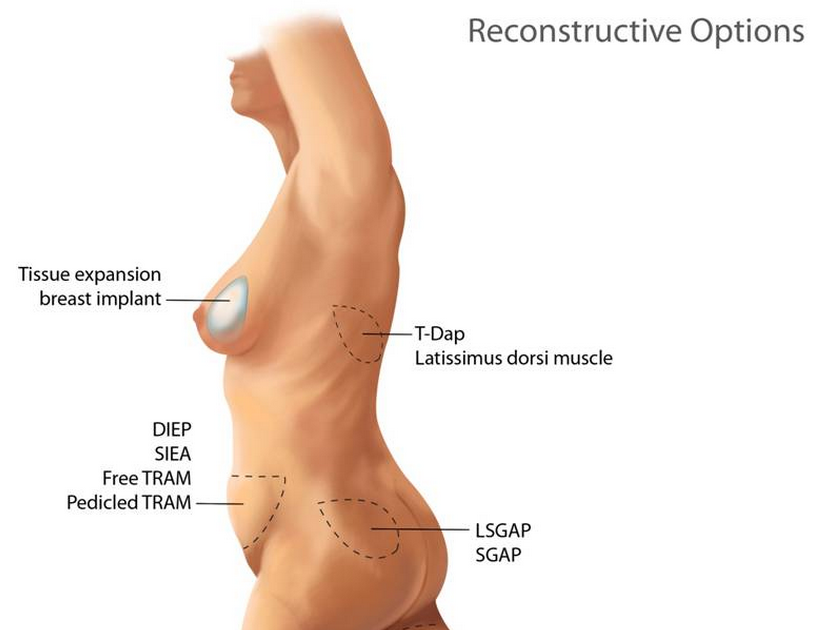
South Bay Plastic Surgeons in Torrance perform a variety of breast reconstruction procedures. This article describes the final four in our series: SGAP, IGAP, TUG and PAP breast reconstruction methods.
The Benefits of Flap Reconstruction Compared with Implant Reconstruction
The primary benefit of flap reconstruction, whether it uses tissue from the back, buttocks, thighs or abdomen, is the ability to utilize tissue from the patient’s own body, which can lead to better healing and/or a more natural appearance. Sometimes additional tissue (flap) is needed to replace or add to skin damaged from radiation.
The Best Patients for SGAP, IGAP, TUG and PAP Breast Reconstruction
- Does not need or has completed radiation treatment, and/or
- Has too little abdominal tissue to use for DIEP flap reconstruction, and/or
- Has scars from previous abdominal surgery that make it impossible to use abdominal tissues for reconstruction, and/or
- Wants to avoid abdominal surgery, and/or
- Has smaller breasts, as less tissue can be grafted from the thighs and buttocks compared to tissue from the abdominal area.
As with other breast reconstruction procedures, patients must be tobacco-free to minimize the risks of anesthesia and to optimize wound healing.
SGAP and IGAP Flaps:
The SGAP and IGAP flap procedures use tissue grafted from the buttocks: 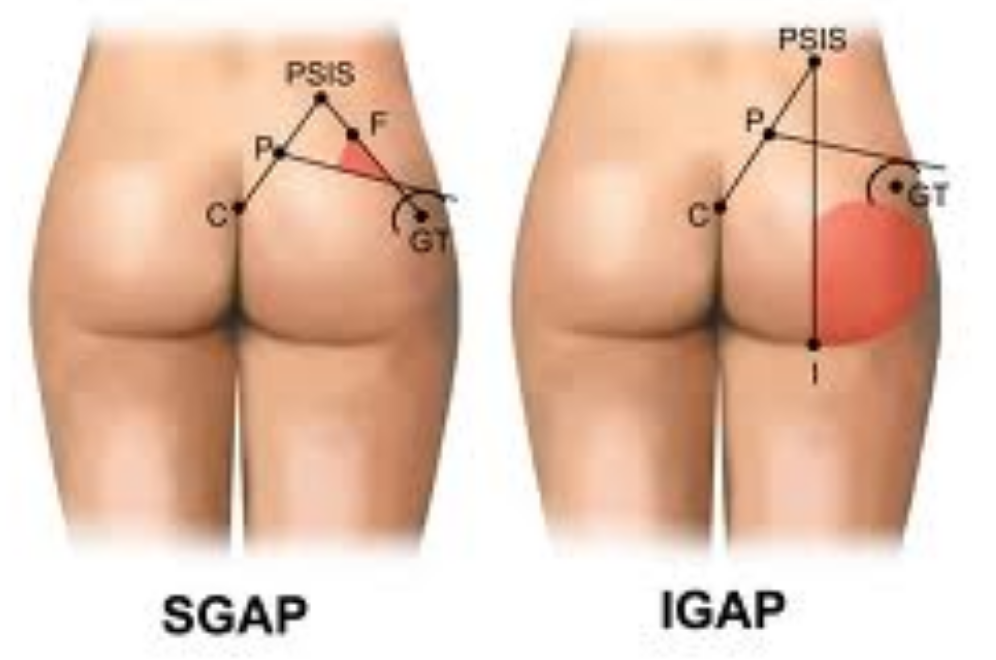
In the SGAP procedure, the tissue is taken from the top area of the buttocks
In the IGAP procedure, the tissue is taken from the lower area of the buttocks
SGAP
SGAP is an acronym for superior gluteal artery perforator. The SGAP breast reconstruction method uses tissue from the top area of the buttocks to create a breast. There is no muscle used in the SGAP procedure. Since the SGAP procedure takes tissue from the top area of the buttocks, the natural contours of your buttocks are preserved.
IGAP
IGAP is an acronym for inferior gluteal artery perforator. The IGAP breast reconstruction method uses tissue from the lower area of the buttocks to create a breast. There is no muscle used in the IGAP procedure. Since the IGAP procedure takes tissue from the lower buttocks, the scar is similar to that of a buttock lift and is generally hidden in the natural fold.
TUG and PAP Flaps:
The TUG and PAP flap procedures use tissue grafted from the thighs:
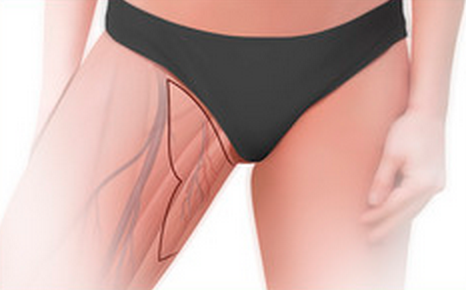
In the TUG procedure, the tissue is taken from the inner upper thigh
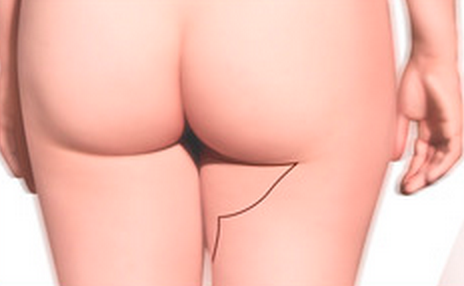
In the PAP procedure, the tissue is taken from the back of the thigh, just beneath the buttock crease
TUG
TUG is an acronym for transverse upper gracilis flap. The TUG breast reconstruction method uses tissue from the inner upper thigh near the groin crease to recreate a breast. The gracilis muscle is also used. The TUG flap is often chosen for women without adequate tissues in the abdominal or buttock area, as well as women with small breasts who do not require a large volume for breast reconstruction. There are two specific benefits of the TUG flap: the scar is well hidden in the groin crease, and the gracilis muscle is not a critical strength muscle, so most patients do not experience weakness after breast reconstruction surgery.
PAP
PAP is an acronym for profunda artery perforator. The PAP breast reconstruction method uses tissue from the back of the upper thigh to recreate a breast. There is no muscle used in the PAP procedure. A benefit of this procedure is a nearly invisible scar, as it’s placed just beneath the buttock crease. In fact, the results are similar to a thigh lift, as the inner thigh will be tighter after a PAP procedure. As with the TUG flap, the PAP procedure is often used for women with small to medium-size breasts. If you have larger breasts, your South Bay Plastic Surgeon may elect to place a breast implant to match the size of your other breast.


Looking for comparisons between sgap and pap flap procedures including risks
Hi Audrey,
Thanks for your question. Please call our office directly and ask for me if you have more questions.
PAP flap: profunda artery perforator flap. Takes tissue from the posterior thigh area just inferior to the buttocks.
Advantatges: concealed donor scar, posterior thigh lifting effect; good for patients who have had extensive abdominal surgery or who lack sufficient tissue in the abdomen for DIEP reconstruction.
Possible complications: seroma, hematoma, fat necrosis; this procedure can accentuate prominent “saddlebags” if flap is not beveled to include subcutatneous soft tissue in this area. Possibility of damage to the posterior femoral cutaneous nerve .
Size limitation: unlike the DIEP flap, the PAP flap has a smaller area from which to harvest and thus a size constraint in reconstruction – usually 350-400g.
SGAP: superior gluteal artery perforator flap. Takes tissue from the top of the buttocks using a “heart-shaped” incision.
Advantages: few. For patients with little abdominal fat and gluteal sag/excess tissue, this can be a reasonable option as it creates a lifting effect for the buttocks.
Disadvantages: in addition to standard post surgical possibilities (seroma, hematoma, infection)– the scar can be visible with low-cut jeans or bikinis; the consistency of the fat is firmer than that of breast tissue, leading to the possibility of a less than completely natural reconstruction.
Sincerely,
Camille